Lice Removal Guide: How to Calculate How Long You Have Had Lice?
Intro:
Having head lice can be a distressing experience, and many people wonder how long they’ve been living with these pests. Determining the duration of infestation can be a crucial part of addressing the issue. This guide will walk you through the life cycle of lice, their symptoms, and methods to estimate the duration of your infestation.
Lice infestation, scientifically known as Pediculosis, is a common condition affecting millions around the globe. With so many people encountering these pesky parasites, it’s crucial to understand how to determine the length of a lice infestation to manage and eradicate them effectively.
What are Lices?
Lice are small, wingless insects that infest the human scalp. There are three types:
- Head Lice (Pediculus humanus capitis): Most commonly found on the scalp.
- Body Lice (Pediculus humanus corporis): Found on clothing and moved to the skin to feed.
- Pubic Lice (Pthirus pubis): Found in the pubic region and occasionally on coarse body hair.

How to Calculate How Long You Have Had Lice?
So how to determine how long you have had lice? By examining the stages of lice present on the scalp, you can estimate the infestation duration. A head with only nits suggests a recent infestation, while the presence of both nits and adults indicates a longer period. Regularly checking for lice can provide insight into the infestation timeline.
Why It Matters to Tell How Long Have You Had Lice?
Understanding the duration of lice infestation aids in selecting the suitable treatment method. Longer infestations may require more aggressive treatments. Moreover, knowing the timeline can help identify the potential source of the infestation, aiding in prevention.
Lice Symptoms
Lice infestations often lead to an itchy scalp, resulting from an allergic reaction to lice bites. Individuals may also experience an itchy sensation and see red bumps around the scalp, neck, and ears.
- Itchy scalp due to lice bites
- Tickling sensation as lice move
- Red bumps on the scalp, neck, and ears
Appearance
Lice are small, wingless parasites, typically brown to grayish-white in hue. About the size of a sesame seed, they can be distinguished from dandruff by their firm attachment to hair. Nits, the lice eggs, have a characteristic yellowish-white oval shape.
- Lice: Small, wingless, brown to grayish-white insects.
- Size: Comparable to a sesame seed.
- Nits: Oval, yellowish-white eggs firmly attached to hair.
- Distinction: Unlike dandruff, lice and nits cling tightly to hair strands.
Lice Life Cycle:
Lice undergo a three-stage life cycle:
- Eggs (Nits): Nits are laid by an adult female lice at the base of the hair shaft. They hatch in 7-10 days.
- Nymph: The baby louse emerges and matures into an adult in 9-12 days.
- Adult: Adult lice can live up to 30 days on the host’s head. A female can lay up to 8 nits per day.
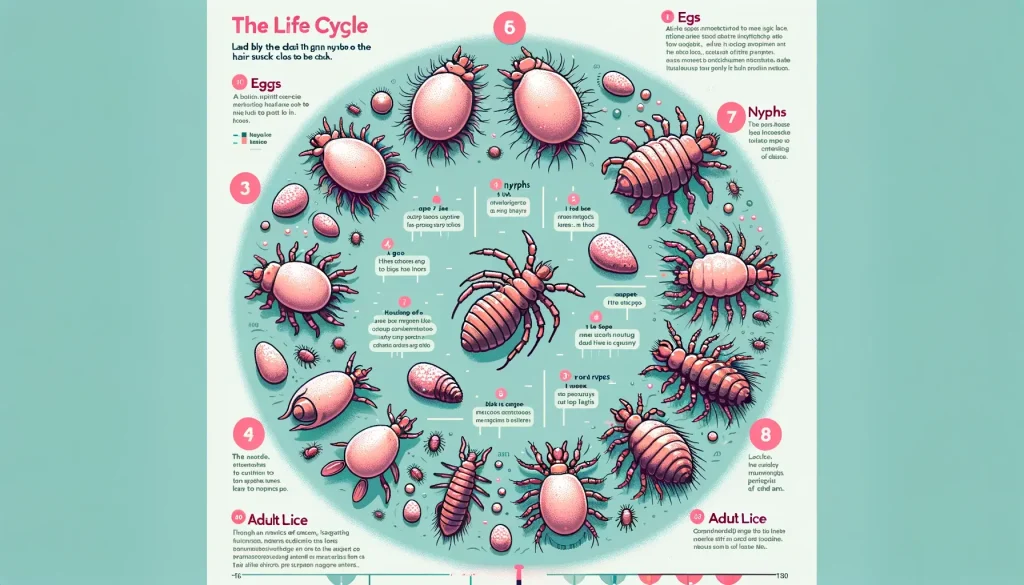
Infestation Timeline
The lifecycle of lice provides clues about the duration of an infestation. Nits hatch within a week, evolving into nymphs, which mature into adults in another week. Discovering mature lice and fresh nits suggests an infestation duration of roughly two weeks.
Initial Stage (Less than 2 weeks):
If you spot only a few nits and no adult lice, this indicates a relatively fresh infestation. Adult lice lay approximately 6 to 10 eggs daily, generally taking around 9 days to hatch. Discovering just a few nits and the absence of adults suggests that you’re likely in the early days of an infestation.
Mid Stage (1.5 to 2 weeks):
Finding both nits and moving nymphs (juvenile lice) without many adult counterparts signals an infestation lasting roughly 1.5 to 2 weeks. Here, the nits have started to hatch, leading to a noticeable increase in the number of nymphs and nits compared to someone who’s just been affected.
Advanced Stage (2 weeks or more):
Observing a mix of nits, nymphs, and adult lice indicates an ongoing infestation of at least two weeks. If you also experience symptoms like persistent itching, it’s plausible that you’ve been harboring lice for four to six weeks or even longer.
Receding or Old Infestation:
If you only spot nits over 1/4 inch from the scalp, it suggests a waning or old infestation. Given that lice eggs predominantly hatch close to the scalp’s warmth, nits found further down the hair shaft often imply a past, possibly treated, infestation, with remnants gradually shifting away from the scalp.
How to Look for Lice in the Hair?
Using a fine-toothed comb, section off the hair and comb close to the scalp. Examine the comb after each stroke. Wetting the hair can immobilize the lice, making them easier to spot. Ensure good lighting or use a magnifying glass.
How to Treat Lice at Home?
To effectively treat lice at home, start with over-the-counter shampoos or creams containing pyrethrin or permethrin. After application, use a fine-toothed nit comb to remove dead lice and nits. Always repeat the treatment after 7-10 days to ensure all lice are eradicated.
How to Prevent and Get Rid of Lice?
Preventing lice infestation requires proactive measures and awareness. It’s essential to avoid direct head-to-head contact, as lice cannot jump or fly. Refraining from sharing personal items can further reduce the risk.
- Avoid Direct Contact: Lice crawl, so direct head-to-head contact is their primary transmission mode.
- Don’t Share Personal Items: Combs, hats, and headphones can harbor lice.
- Regular Hair Checks: Especially during lice outbreaks at schools or among peers.
- Wash Belongings: Regularly launder items in hot water, especially if there’s a known outbreak.
- Often, clean your hair with a lice comb.
When to See a Doctor to Treat Lice?
If over-the-counter treatments fail or if the scalp shows signs of infection, it’s crucial to see a doctor. They can provide prescription treatments and offer guidance on managing severe or persistent infestations.
FAQs:
Conclusion:
Head lice infestations can be unnerving, but understanding their lifecycle and recognizing symptoms early can aid in effective treatment. Regular checks, preventive measures, and prompt action can help manage and mitigate lice impacts.






